Stakeholder Engagement
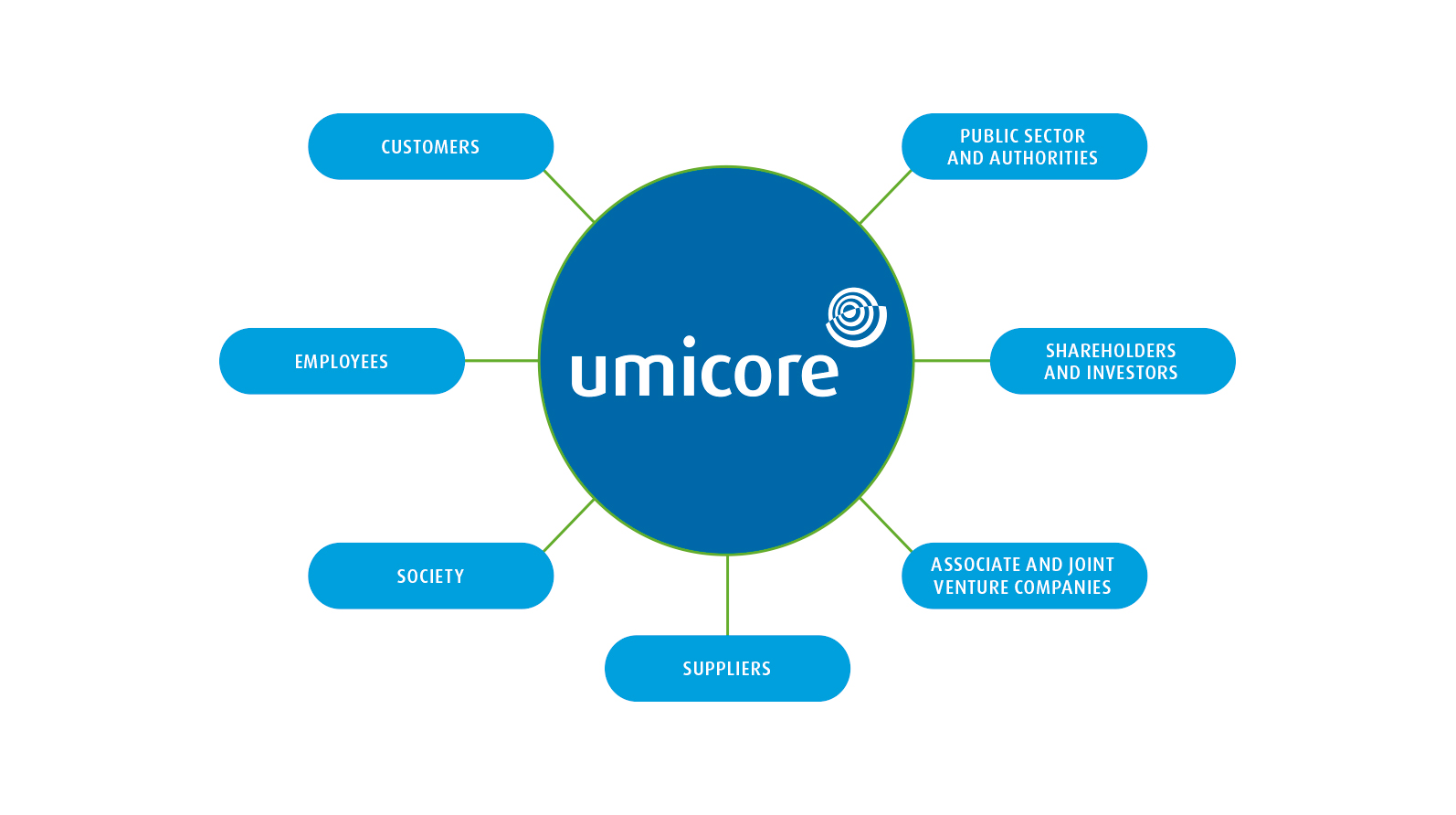
Umicore is a publicly listed company. As such, we interact with many parties who have an interest in the way we conduct business. The relationship that we foster with these parties or stakeholders has a direct impact on our success.
Stakeholder engagement at Umicore is based on a localized approach whereby all sites are required to identify their respective stakeholders and establish suitable ways of engaging with them. In many cases, such as the dialogue with customers and suppliers, the stakeholder relationships are primarily managed by the business units themselves, in line with our decentralized approach to unit management.
The management board receives feedback from stakeholders in several ways, ranging from direct feedback from visits to customers, suppliers, employees and investors, to information provided by the business units, departments or workers’ representatives during their regular briefings to senior management. Other forms of input include periodic employee survey results.
The Horizon 2020 strategy represents a strong focus on what is of material importance for Umicore through 2020. The development of the strategy has involved a specific stakeholder approach, described in the materiality assessment process in this chapter.
Umicore is an active participant in various industry associations through which we engage with policy makers to contribute to a better understanding of industry-related issues. These associations are also important platforms for Umicore to contribute to broader, industry-wide action on sustainable development.
On a less formal level, members of our senior management are often called upon or volunteer to participate in public forums to discuss our business strategy and sustainable development approach. Such events provide the opportunity to interact with various groups including business leaders, academics and civil society.
Umicore’s main stakeholder groups are highlighted and have been categorized in broad terms, using generic stakeholder categories that apply to most industrial organizations. Also shown are the nature of the transactions that occur and a brief description of the dialogue between Umicore and the stakeholders.

Umicore materials can be found in a variety of applications that deliver solutions for cleaner air and increased e-mobility.Umicore’s unique closed-loop services turn waste metals into a resource. To be the preferred partner of our customers, we work closely with them to develop, produce and recycle metal-related materials for material-based solutions tailored to their needs.
Umicore materials can be found in a variety of applications that deliver solutions for cleaner air and increased e-mobility. Umicore’s unique closed-loop services turn waste metals into a resource. To be the preferred partner of our customers, we work closely with them to develop, produce and recycle metal-related materials for material-based solutions tailored to their needs.
We provide advanced products that are built on our customers’ specific performance, environmental and sustainable sourcing needs, including development of bespoke solutions when needed. Beyond this customer-oriented approach, we provide close collaboration across all regions to deliver a sustainable and secure supply of high-quality products and services. Umicore has an international customer base and the presence to support them in both growing and established markets. Our high investments in R&D provide advanced and efficient production and process technologies that enable our customers to meet the most stringent sustainability demands and ambitions.
Ongoing interaction with customers is managed by the business units. In addition to this close contact, all business units have a customer feedback process to periodically gauge customer satisfaction.
Countries with Umicore customers
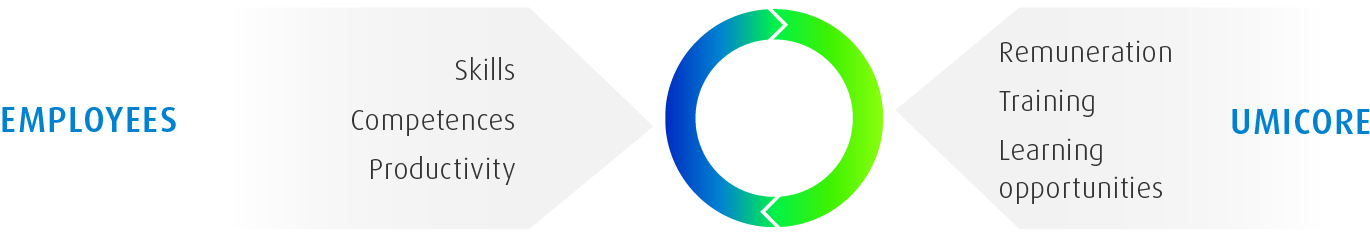
Umicore employs 10,859 people worldwide. Because our employees are key to our success, we invest significant resources in ensuring we are an employer of choice in all the regions where we operate. In 2020, Umicore paid a total of € 798 million in salaries and other benefits to the employees of fully consolidated companies, of which € 97 million in social security payments.
Umicore is committed to providing competitive salaries and working conditions to its employees and to providing occupational and professional training opportunities. Employees are expected to adhere to the principles and policies outlined in The Umicore Way and Code of Conduct. Open dialogue is promoted within the company and includes an opinion survey every 3 years.
Umicore respects the principle of collective bargaining wherever it is requested. While such practice is commonplace in Europe, in other locations collective bargaining mechanisms and trade unions may be less common or face local legal restrictions. In 2019, Umicore renewed the sustainable development agreement with the international union IndustriALL on the global implementation of its policies on human rights, equal opportunities, labor conditions, ethical conduct and environmental protection. The agreement allows trade unions to participate constructively in the pursuit of these objectives. A joint monitoring committee composed of both parties oversees the implementation of the agreement.
Company-wide communication channels include intranet and company and business unit newsletters. Umicore operates a Group-wide learning management platform called “MyCampus”.
In salaries & other benefits
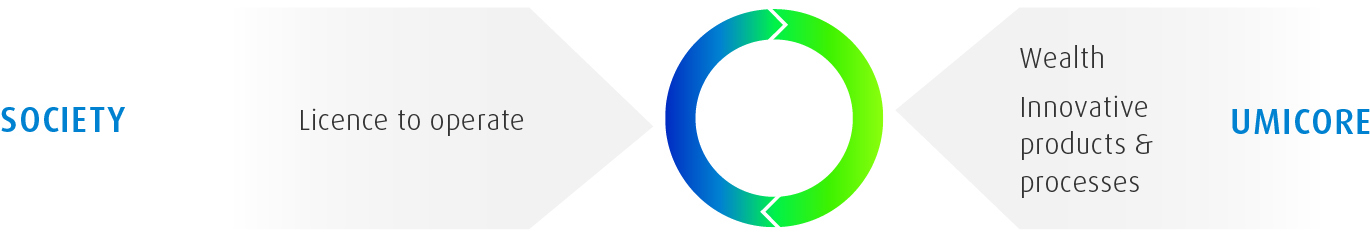
Umicore can only continue operating if it has the license to do so from society and we the utmost to operate in a way that promotes sustainable development, going beyond the legally defined boundaries set for all companies. We set our own standards, applicable across the Group, often surpassing the legislative demands in many areas where we operate. Umicore also strives to develop materials that enhance quality of life and specifically addressing certain critical environmental or societal challenges.
Contact with the communities where Umicore operates is the most direct way that we interact with society. Open and transparent dialogue with such communities is an integral part of our stakeholder engagement. Through employment, Umicore participates in the generation of wealth in the areas where it operates. Although wealth generation is an obvious benefit, the way in which this wealth is generated is also of great importance. We strive to be top employer wherever we operate. ivil society groups periodically declare a stake in our operations and the way we do business. Umicore welcomes such interest and attempts to engage openly and constructively.
Umicore makes voluntary contributions at site and Group-level to a range of charitable causes. We manage Group-level engagement efforts through a Group Donations Committee that has the mandate of engaging with civil society groups and determining the extent of partnerships. For information on these initiatives in 2020 see Giving Back to Society.
Donated to charitable causes
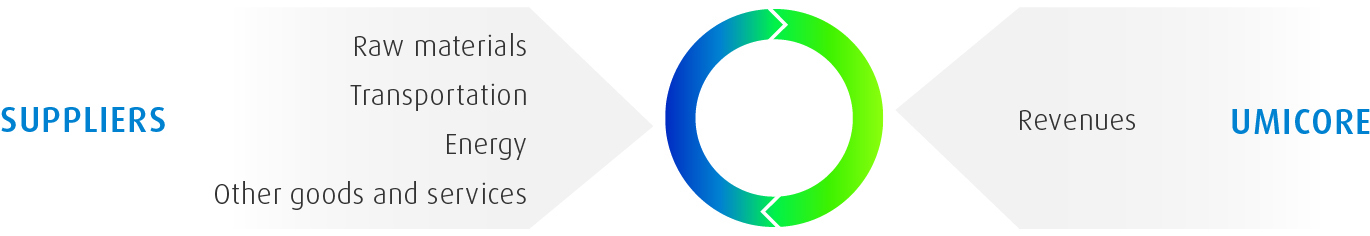
Umicore operates through 3 business groups on 5 continents. These business groups not only require materials to make their products but also energy, transportation and a range of other services. Overall, Umicore has over 18,000 suppliers across over 90 countries. These suppliers benefit from our presence as a customer: in 2020, Umicore paid these suppliers € 18.7 billion (including the metal content of raw materials).
We are engaged in a constant dialogue with our suppliers to define technical specifications and to ensure mutually acceptable terms and conditions for continued partnership, such as prompt and uninterrupted delivery of materials/services. The business units are responsible for the purchase of raw materials while the corporate Purchasing and Transportation department works to ensure that transportation, energy and other provisioning needs are met.
Our approach is shaped by our Sustainable Procurement Charter. This charter is complemented by specific approaches or frameworks for some critical raw materials. Our Horizon 2020 strategy includes an objective on sustainable supply that builds on the experience gained through our previous objective on sustainable procurement. For information, see Value Chain & Society.
Paid to suppliers worldwide
Umicore has investments in various business activities over which it does not exercise full management control. Associate companies are those where Umicore has a significant influence over financial and operating policies, but no control. Typically, this is evidenced by ownership of between 20% and 50% of the voting rights, while joint ventures usually entail a 50:50 split in ownership and control. Joining forces is a way to speed up technological developments or gain access to specific markets.
Where management control is not exercised by Umicore, we are able to guide and control the management and monitor business developments through representation on the board of directors. Although we cannot impose our own policies and procedures on any associate (or indeed any joint venture where we do not possess majority voting rights), our expectations that the operations be run in accordance with the principles of the Umicore Way are clearly communicated.
Umicore is rigorous in safeguarding any intellectual property that is shared with associate or joint venture partners. For a full list of associate and joint venture companies, see note F17.
Associate companies
In 2020 Umicore engaged with a variety of stakeholders to introduce the technology fundamentals of the material solutions we offer to our customers. Umicore coordinates and fosters a range of interactions in the countries and regions where we are operationally active. We focus on policy development supporting the introduction of clean mobility supporting the global energy transition to reduce climate impact. In addition, we contribute to a better understanding and faster implementation of circular economy models in the applications related to Umicore activities. Continuous innovation is crucial to improve our products and services and therefore we also engage in national and international programs and initiatives that develop longer-term technology roadmaps serving as a basis for collaborative funding opportunities. As a result, Umicore was approved as a partner in the first Important Project of Common European Interest for Batteries (IPCEI) starting from early 2020. Part of the innovation and upscaling activities for battery materials and battery recycling in Belgium, Germany and Poland will be funded by the national governments. Umicore is mindful of the sensitivity of taking positions on issues of public interest and has developed guidelines to do so responsibly through the industry groups to which we are affiliated. Well-developed science and facts form the basis of the opinions and position we take.
Umicore paid € 79 million in taxes on our 2020 operations and with our employees contributed € 97 million in social security payments. Umicore regularly enters scientific partnerships with public institutions such as universities with the primary aim of furthering research projects or providing expert advice on technology directions. Partnerships and research grants are occasionally contracted with public organizations. As a matter of policy, Umicore does not make donations to political parties or organization.
Taxes paid on our 2020 operations
KEY MEMBERSHIPS
A3M (L’Alliance des Minerais, Minéraux et Métaux); Agoria (Belgian multi-sector federation for the technology industry); American European Community Association (AECA); Bebat; Belgian Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (BICC&I); Belgian industrial Research and Development (BiR&D); Belgium-Japan Association & Chamber of Commerce (BJA); Eurometaux (European Non-Ferrous Metals Association); European Industrial Research Management Association (EIRMA); European Round Table of Industrialists (ERT); ETION; Federation of Belgian Industrial Energy Consumers (FEBELIEC); Flemish Aerospace Group (FLAG); Flemish Network of Enterprises (Voka); Flanders-China Chamber of Commerce (FCCC); Global Legislators for a Balanced Environment (GloBE EU); Metalle pro Klima (WirtschaftsVereinigung Metalle); TransAtlantic Business Council (TABC); Verbond van Belgische Ondernemingen (VBO); Vlaamse Technische Kring (VTK); World Economic Forum (WEF).
Associacao dos Fabricantes de Equipamentos para Controle de Emissoes Veiculares da América do Sul (AFEEVAS); Association for Emissions Control by Catalyst (AECC); Catalyst Manufacturers Association, Japan (CMAJ); Committee of Vehicle Emission Control in China (CVEC); Emission Controls Manufacturers Association, India (ECMA); European Precious Metals Association (EPMF); Hydrogen Council; Hydrogen Europe; Manufacturers of Emission Controls Association (MECA); Verband der Automobilindustrie (VDA); Verband der Chemischen Industrie e.V. (VCI).
Battery Europe Partnerhip Association (BEPA); Cobalt Institute; Cobalt REACH consortium; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Galvano- und Oberflaechentechnik (DGO); Energy Materials Industrial Research Initiative (EMIRI); European Association for Battery, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (AVERE); Nickel Institute; Nickel REACH consortium.
European Battery Recycling Association (EBRA); European Electronics Recyclers Association (EERA); European Precious Metals Federation; Fachvereinigung Edelmetalle (German Precious Metals Association); Global Battery Alliance (GBA); International Platinum Group Metals Association (IPA); International Precious Metals Institute; Minor Metals Trade Association; Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC); The European Association of Advanced Rechargeable Batteries (RECHARGE); The International Platinum Group Metals Association (IPA); The London Bullion Market Association (LBMA); The London Platinum and Palladium Market (LPPM); Vereniging Nederlandse Metallurgische Industrie (VNMI).


 Belgium
Belgium Germany
Germany Worldwide
Worldwide