Managing risk effectively

Each business unit operates in an environment which carries specific growth expectations and differing degrees of market and technological uncertainty that could impact strategic objectives.
As such, the primary source of risk and opportunity identification lies within the business units. Similarly, each business unit is responsible for mitigation of its own risks. Mitigating actions are systematically reported corresponding to the respective strategic objectives and identified risks.
Specific corporate departments are also tasked with managing and mitigating certain risks under the auspices of the Management Board. These risks cover Group-wide elements that extend beyond the purview of individual business units. These include environmental risks, financial risks, etc.
OUR INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEM
Internal control mechanisms exist throughout Umicore to provide management with reasonable assurance of our ability to achieve our objectives. They cover:
Effectiveness and efficiency of operations
Reliability of financial processes and reporting
Compliance with laws and regulations
Mitigation of errors and fraud risks
Umicore adopted the COSO framework for its Enterprise Risk Management and has adapted its various constituents within its organization and processes. “The Umicore Way” and the “Code of Conduct” are the cornerstones of the Internal Control environment; together with the concept of management by objectives and through the setting of clear roles and responsibilities they establish the operating framework for the company.
Specific internal control mechanisms have been developed by business units at their level of operations, while shared operational functions and corporate services provide guidance and set controls for cross-organizational activities. These give rise to specific policies, procedures and charters covering areas such as supply chain management, human resources, information systems, environment, health and safety, legal, corporate security and research and development.
Umicore operates a system of Minimum Internal Control Requirements (MICR) to specifically address the mitigation of financial risks and to enhance the reliability of financial reporting. Umicore’s MICR framework requires all Group entities to comply with a uniform set of internal controls in 12 processes.
Within the Internal Control framework, specific attention is paid to the segregation of duties and the definition of clear roles and responsibilities. MICR compliance is monitored by means of self-assessments to be signed off by senior management. The outcome is reported to the Management Board and the Audit Committee.
Out of the 12 control cycles, 2 cycles (Procure To Pay, Information Technology Management) were assessed in the course of 2020 by the 99 control entities currently in scope. Risk assessments and actions taken by local management to mitigate potential internal control weaknesses identified through prior assessments are monitored continuously. The Internal Audit department reviews the compliance assessments during its missions.

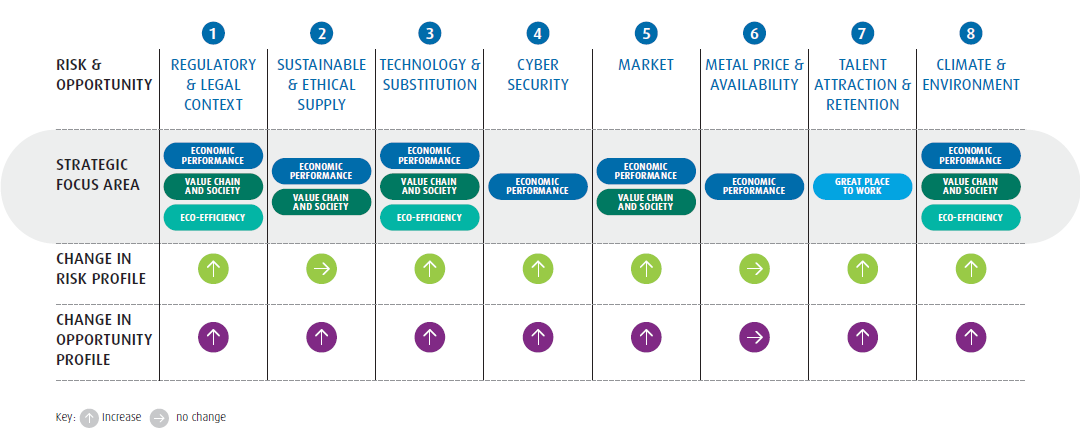

POTENTIAL IMPACT
Umicore is exposed to changes in the regulatory environment in the countries or regions where it operates. Umicore’s businesses stand to benefit from certain regulatory trends, notably those regarding more stringent emission controls for vehicles, low carbon mobility, electrification and enforced recycling of end-of-life products.
Some regulations, such as environmental or product-related laws, can present operational challenges, higher costs and a potentially uneven competitive environment.
Data protection, IP and IP protection-related matters impact technology-driven businesses.
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
Worldwide, changes to existing product-related legislation and the introduction of new legislation might impact our business. Although the European REACH regulation is still the most relevant for Umicore, Korean REACH is gaining importance. For more information, see note V4.
The push towards clean mobility is stronger than ever, with various governments including green recovery measures and stimuli for cleaner mobility in their crisis recovery packages, in particular in Europe and China, and regulatory initiatives to protect air quality and reduce greenhouse gas emissions in several regions. Europe recently reconfirmed its ambition to achieve zero-emission mobility and remains committed to increasingly more stringent CO2 emission targets. In China, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology announced an extension of the New Energy Vehicle (NEV) subsidy plan from 2020 until end 2022. It also confirmed its long-term commitment to achieve a target penetration rate of 20% NEVs in 2025 and 50% by 2035, which is likely to boost electrification in the coming years.
Geopolitical conditions, trade and tariffs continue to be a factor in Umicore’s trans-border activities.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
Umicore provides continuous training on regulatory requirements to ensure compliance with applicable legislation.
To ensure ongoing compliance with environmental legislation on our industrial sites, Umicore has a well-established EHS compliance audit program and constantly monitors changes in legal requirements where we operate. For more information, see Statements, note E8.
Umicore continues to play an active role in informing legislators of various emission control technologies for both diesel and gasoline powered vehicles, to help legislators make informed decisions about future emission and testing norms.
We monitor that our products have the freedom to operate and we proactively manage our patent portfolio. Umicore trade compliance closely follows and responds to global trade conditions.
Umicore monitors closely all changes in interpretation as well as guidance documents that might affect its REACH implementation strategy. In 2020 we submitted 27 additional substances for registration under REACH due to new business developments. As part of regular maintenance, we updated 76 REACH dossiers. Umicore has submitted 2 registrations in Korea in 2020 for priority chemical substances.

POTENTIAL IMPACT
Umicore requires certain metals or metal-containing raw materials to manufacture its products and feed its recycling activities. Some of these raw materials are comparatively scarce and require very specific sourcing strategies. Obtaining adequate supplies of these materials is important for the ongoing success and growth of our business.
Some metals are also found in regions facing social challenges. Trading in precious metals and minerals can be used to finance armed conflict, cause human rights abuses, draw upon forced or child labor and support corruption and money laundering. We ensure that procurement of minerals from conflict-affected and high-risk areas is in line with Umicore’s values, while providing an advantage to our customers.
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
Existing and upcoming laws aiming to drive the responsible sourcing of conflict minerals (tin, tantalum, tungsten and gold), have increased the visibility and concern on the conditions around conflict mineral sourcing in public discourse.
COVID-19 and the measures taken to contain contagion could have an impact on the availability of materials and in general on the supply chain.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
Only limited and temporary impacts due to COVID-19 were reported on Umicore’s supply chain.
Umicore implemented policies and measures covering human rights, the right for workers to organize, collective bargaining, equal opportunities and non-discrimination, banning of child labor, banning of forced labor, consistent with International Labour Organisation (ILO) standards. These commitments are supported through a Global Framework Agreement on Sustainable Development with IndustriALL Global Union which was renewed in 2019.
In addition to existing policies and charters such as the Umicore Code of Conduct, Human Rights Policy and Sustainable Procurement Charter, Umicore also has a specific policy for “Responsible global supply chain of minerals from conflict-affected and high-risk areas”.
In 2020, Umicore again received third-party validation for the application of its Sustainable Procurement Framework for Cobalt, which is aligned with the OECD ‘Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas’. Umicore continues to ensure that its production operations are certified as conflict-free and receives site and metal-specific responsible sourcing certifications from the LBMA and RJC. For more information, see note V3.
Umicore remains the first cathode material producer to offer certified materials from a clean and ethical origin to its customers.
In 2020, Umicore achieved a Platinum EcoVadis rating, placing the group among the top 1% of their industry peers.
We use our long-standing and growing experience in sustainable sourcing to advocate for more responsible practices in industry. To read more about some of our advocacy work, see Stakeholder Engagement.

POTENTIAL IMPACT
Umicore is a materials technology group with a strong focus on the development of innovative materials and processes. The choice and development of these technologies for existing and new markets represents the single biggest opportunity and risk for Umicore.
Achieving the best cost-performance balance for materials is a priority for Umicore and its customers. There is always a risk that customers will seek alternative materials for their products should those of Umicore not provide this optimum balance. The risk is especially present in businesses producing materials containing expensive metals (especially those with historically volatile pricing characteristics).
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
Trends in rechargeable battery materials for automotive applications have underscored that NMC material platforms with increasing nickel content as well as medium nickel low cobalt content are the technologies of choice for customers in current and upcoming electrified vehicle platforms. Besides the focus on high performing battery materials, novel processes are being developed to decrease cost and environmental impact across the entire battery value chain.
In vehicle emission control, regulatory debates have reinforced the need for a broad spectrum of technologies for both gasoline and diesel applications. These technologies need to be optimized for performance and for cost.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
Every year, the Management Board identifies innovation projects which are key to achieving our short term and long-term growth ambitions and cover product and process developments. These technologies are followed up closely by management to ensure on time delivery of new and innovative products to the market.
Previous years’ R&D investments have brought great success and created a space to expand R&D positioning to adjacent and new markets within Umicore’s field of expertise. In 2020, overall spend was equivalent to 6.9% of revenues. The Innovation Fit for Future program focusing on innovation excellence best practices protects Umicore’s technology leadership and future growth.
Umicore patents disruptive technologies. In 2020, Umicore registered 63 new patent families.
For more information, see Research, development & innovation.

POTENTIAL IMPACT
Umicore’s production plants and services highly depend on the availability of IT services.
Unavailability of services, disruption of the supply chains or interruption of our production facilities due to cyber-attacks could have a major impact on our customers. A compromise in the confidentiality of intellectual property would negatively impact our competitive advantage. Unauthorized modification of financial data would jeopardize accurate reporting to shareholders.
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
Cyber-attacks may be very focused and advanced. The expanding threat landscape and expanding digital footprint is leading to an increase in cyber-attacks. Several cases of industrial manufacturing businesses being interrupted for several weeks as the result of a cyber incident have been extensively covered in the media. In addition, due to the increased use of a digital work environment (on site and at home), the role of IT services in delivering seamless access to all corporate resources as well as ensuring information security is more important than ever.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
Umicore continues to regularly assess and improve its information security, and the state of cyber resilience of its IT landscape, against evolving threats.
A security roadmap is being implemented which includes projects in preparation for an ISO27001/2 certification and initiatives to increase awareness across the Group on the importance of information and cyber security. Third party expert security assessments are made and the corporate cyber security team is being expanded. Umicore increases its investments in security-related IT systems and applications such as backup processes, virus and access protection, authentication and encryption tools. Security-related IT controls are being extended and are tested as part of Umicore’s external audit process.
The state of cyber security is reported to the Management Board semi-annually and is followed-up by the Audit Committee.

POTENTIAL IMPACT
The main industries served by Umicore are automotive (clean mobility materials, recycling), consumer electronics (rechargeable battery materials, recycling, coating and electroplating solutions) and non-ferrous metal mining and refining industries (recycling activities). Umicore is sensitive to any major growth or global reduction in activity levels or market disruptions in these industries.
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
In 2020, the global automotive industry was significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic with a marked contrast between the first and the second half of the year.
In the first half of 2020, car OEMs had to shut down their production plants and close their dealerships in several key regions as a result of government imposed lock-downs. Global car demand started to pick up again in the second half of 2020, albeit with discrepancies between the regions in terms of timing, speed and intensity of the recovery.
Car production in the second half grew by more than 40% sequentially (yet declined by 2% compared to the second half of 2019), with China being the clear driving force behind the global recovery. Other key markets started to pick up later and more gradually and still recorded negative growth for the second half of the year.
The sharp economic contraction and the lower industrial production induced by COVID-19 also had a significant and a more prolonged impact on the heavy-duty diesel market segment in 2020 except in China.
The global EV market was profoundly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic in the first half of the year and rebounded in the second half of the year, primarily driven by strong EV growth in Europe and, later in the year and to a lesser extent, by increasing EV sales in China.
In China, battery demand for EVs remained bleak until the summer and turned positive in the second half of the year, albeit compared to a depressed second half in 2019. The demand for cathode materials for EVs has lagged the anticipated growth in 2019 and 2020, resulting in significant excess capacity and pressure on the pricing environment.
In Europe, battery demand for EVs recorded strong momentum throughout 2020, in particular in the second half of the year, and doubled compared to 2019. This growth was driven by new models launched by car OEMs to comply with the more stringent CO2 directive, local incentives for EV buyers in several countries as part of their recovery plans and more environmentally-friendly choices by consumers when purchasing a new car.
The slowdown in consumer electronics demand continued along with a reduced demand for NMC cathode materials used in energy storage applications.
In recycling, our process remains unique, supported by high metal prices and high activity levels with favorable trading conditions in 2020, despite the COVID-19 crisis. The overall supply of industrial by-products remained favorable over the period, despite the temporary shutdowns of certain mining activities in response to COVID-19. Also the supply of end-of-life materials remained strong.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
Umicore is delivering on its growth strategy in clean mobility materials and recycling.
Despite the severe disruption brought by the COVID-19 pandemic in its end-markets, Umicore posted its strongest financial performance ever, boosted by an exceptional metals price environment. This underscores Umicore’s resilience and the merits of the Horizon 2020 strategy that builds on the complementarity of our activities. After a solid performance in the first half of 2020, with a strong result in Recycling offsetting the impact of the automotive industry downturn, the second half of the year was marked by a strong sequential improvement in revenues and earnings. This has been driven by continued robust operational performance and buoyant metal prices, and strong growth in Catalysis, thanks to Umicore’s strong market position in gasoline technologies for light-duty vehicles, particularly in China and Europe, as well as higher sales of heavy-duty diesel and fuel cells catalysts.
Umicore should continue to benefit disproportionally from the accelerating penetration of electromobility given our broad portfolio of material technologies certified for the most stringent automotive requirements and our industrial-scale production capabilities.
For more information, see Economic Review.

POTENTIAL IMPACT
Umicore’s earnings are exposed to risks relating to the prices of the metals which we process or recycle. These risks relate mainly to the impact that metal prices have on the surplus metals recovered from materials supplied for recycling, and concern platinum, palladium, rhodium, gold, silver and a wide range of base and specialty metals. For some metals quoted on futures markets, Umicore hedges a proportion of its forward metal exposure to cover part of the future price risks.
Umicore also faces transactional price risks on metals. The majority of its metal-based transactions use global metal market references. If the underlying metal price were constant, the price Umicore pays for the metal contained in the raw materials purchased would be transferred to the customer as part of the price charged for the product. However, because of the lapse of time between the conversion of purchased raw materials into products and the sale of products, the volatility in the reference metal price creates differences between the price paid for the contained metal and the price received. Accordingly, there is a transactional exposure to any fluctuations in price between the time raw materials are purchased (when the metal is “priced in”) and the time the products are sold (when the metal is “priced out”). The Group’s policy is to hedge the transactional risk to the maximum extent possible, primarily through forward contracts.
For more information on the structural risk and on the transactional and inventory risk related to the metal prices, see note F3.
Materials produced by Umicore contain precious or scarce metals which are partly sourced from in house recycling operations and, for the balance, procured from primary metal producers. Umicore’s ability to procure the required quantity of such metals is key to determine its ability to produce the materials which have been ordered by the customers.
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
Prices for precious metals strengthened further in 2020, reaching historically high levels for precious metals and PGMs. The price of rhodium in particular increased significantly in the second half of the year, in a context of tight supply and high demand from the car industry.
Demand for cobalt containing products was mixed in 2020, severely hit by the COVID-19 crisis in the first half of the year, showing first signs of recovery in the second half. , Cobalt price remained stable over the course of the year.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
Over the course of 2020 and early 2021, Umicore entered into additional forward contracts securing a substantial portion of its structural price exposure for certain precious metals in 2021, 2022 and 2023, thereby increasing earnings predictability. For 2021 and 2022, approximately two thirds of the expected gold and palladium exposure and somewhat less than half of the expected silver exposure have been locked-in. In addition, close to one third of the expected platinum exposure for 2021 has been hedged. In spite of the absence of a liquid futures market, Umicore has entered into forward contracts locking in a minority of its expected 2022 and 2023 rhodium exposure.
Umicore is continuously increasing production of precious and scarce metals from its recycling capabilities, thereby securing a significant proportion of its metals needs. In addition, the group maintains close commercial relationships with leading primary metals producers from which it procures metals through annual or evergreen contracts.

POTENTIAL IMPACT
The attraction and retention of skilled people are important factors in enabling Umicore to fulfil its strategic ambitions and to build further expertise, knowledge and capabilities in the business. Being unable to do so would compromise our ability to deliver on our goals.
The Horizon 2020 strategy was predicated on growth for Umicore, especially in Asia where labor markets are highly competitive and fluid. Umicore’s challenge is to attract and retain talent at all sites and in all regions on a sufficient scale and at an appropriate pace.
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
In 2020 the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic severely affected people, society and industries globally.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
In response to the COVID-19 outbreak, Umicore rolled out its business continuity plans and took precautionary measures to keep its people healthy and to ensure that the workplace is safe. Umicore rapidly adjusted its production capacity where needed and furloughed part of its workforce; when all production plants resumed operations, most furloughed employees returned to work. In administrative positions, working from home was adopted.
Umicore introduced strict hygiene and other precautionary measures in its facilities worldwide in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and delivered surgical masks for private use to the homes of all employees worldwide at a time when they were unavailable on the open market. A dedicated task force continues to monitor its operations globally with a focus on protecting employees’ health.
To meet recruitment needs in this COVID-19 context, we moved to virtual recruitment and virtual onboarding wherever possible. Operators were recruited and onboarded with utmost safety and health measures.
Umicore ensured continued safety trainings, both virtually and in small groups to respect health measures. Other trainings, including on leadership and development, were delayed while adjusting the offering to the digital delivery in a virtual context but did continue in the second half of 2020.

POTENTIAL IMPACT
Climate and environment impacts are mostly related to our supply of primary raw materials or to our suppliers’ extraction of these primary raw materials. Easy-to-mine deposits are becoming increasingly scarce and ore bodies poorer. Many specialty metals required for new, environmentally-friendly technologies can only be obtained as a by-product of other metals. Treating complex materials from above-ground sources, such as industrial residues and end-of-life materials, is increasingly important.
Climate change causes extreme natural events, chronic deviations in mean temperatures and precipitation patterns, and rising sea levels. This could impact our sites or supply chain.
Increasingly stringent regulations on energy use and emissions can induce higher operational costs.
Our license to operate is predicated on managing the impact of our operations in the communities where we operate. Historical industrial activity requires active management and remediation.
CHANGE IN CONTEXT
Civil society and political discourse are increasingly demanding that business takes an active role in mitigating climate change. In the context of COVID-19, the attention on environmental and climate-related performance of private sector and industry has increased, as has attention around developing a “green recovery”.
The ongoing transition to a lower carbon economy continues to present Umicore with opportunities to expand and develop processes in ways that can mitigate or address climate change and environmental risks.
MEASURES TAKEN BY UMICORE
Umicore plays a key role in the transition to a low-carbon future as our materials tackle global trends for clean air and e-mobility, and our closed loop business model tackles resource stewardship.
Our facility in Hoboken is the world’s largest and most complex precious metals recycling operation, processing over 200 types of raw material and recovering over 20 different metals. We ensure that a high volume of our metals come from secondary sources – production scraps, residues and end-of-life materials. We can also recycle customers’ residues and production scrap to help them maximize their material efficiency and then transform the recovered materials into new products. In total we recover 28 metals from our closed loop activities and we continue to adapt our processes to recycle new and more complex end-of-life products. Our high yield recycling process continues to be a driving force in resource efficiency and contributing to the circular economy.
Our global footprint and diverse site locations reduce our exposure to physical risks. New sites have been chosen considering proximity to customers, access to skilled workforce, excellent logistics, infrastructure and green energy.
Umicore performs life cycle assessments on all products and services on a rolling and ongoing basis to sharpen insight on environmental performance, through the right choice of the chemistry, energy mix, and raw materials, including recycled materials. For the new battery production plant in Poland, Umicore maintains the commitment that electricity will be from renewable sources.
We ensure that our current activities keep to the most stringent environmental standards for air and water and work every year to improve our energy efficiency and environmental footprint despite our growth and increased production. For more information, see Environmental Statements .
Umicore manages its historical environmental legacy, ensuring adequate financial provisions that are reviewed twice a year. For more information, see notes E7 and F29.
In 2020 Umicore continued strategic preparation work on climate and environment-related impact.


 Belgium
Belgium Germany
Germany Worldwide
Worldwide