
Society



Advocating for a more sustainable future
Our mission of Materials for a Better Life drives us to develop material solutions for society’s most pressing issues while we strive to maximize our positive impact.
The Umicore Way is the cornerstone of everything we do at Umicore and outlines our commitments to society, while our mission of Materials for a Better Life drives us to develop responsible and sustainable material solutions. In addition to the materials we produce, Umicore also incorporates various business practices to ensure that we have a positive impact on society.
Supporting policy developments
In the countries and regions in which Umicore is operationally active, we support policy developments that bolster clean mobility and the global energy transition to reduce climate impact. In addition, we contribute to better understanding and faster implementation of circular economy models in the applications related to Umicore activities.
In this respect Umicore collaborates with the Trade Committee of Eurometaux and with the European Commission to define minimum compulsory due diligence requirements for the entire value chain Another example is the contribution Umicore makes to the development of the new European waste shipment regulation in order to stimulate the circular economy. The new regulation will allow more efficient processing of hazardous waste while keeping stringent requirements.
Building networks
To boost our efforts, Umicore participates in many partnerships and knowledge-sharing platforms. We regularly enter into scientific partnerships with public institutions such as universities, with the primary aim of furthering research projects or providing expert advice on technology directions. Partnerships and research grants are occasionally contracted with public organizations. In 2022, these partnerships included IMEC, the Queensland University Australia.
Memberships
Umicore is also a member of various industry associations often sitting on the executive and board level. Such memberships enable us to provide input into strategic initiatives and the regulatory agenda based on innovation and technology advocacy, and market and business insights.
Our CEO is currently a member of three World Economic Forum CEO Communities including: Chemical and Advanced Materials Industry Governors Community comprised of chairs and chief executives from leading partner companies who meet during the WEF in Davos.
He is also part of the CEO Action Group for the European Green Deal – a high-level platform for business leaders to support positive action for the climate, as well as a member of the Alliance of CEO Climate Leaders a global community of CEOs who advocate bold and proactive action to ensure a smooth transition to a low-carbon and climate-resilient economy.
In Europe, Umicore has also actively participated and supported the creation of the European Battery Alliance (since 2017) and the Battery European Partnership Association (BEPA). The latter is the public-private entity that supports the European Commission in defining the technology roadmaps as well as the research and innovation priorities to be funded in the 2021-27 timeframe (under the Horizon Europe program). Umicore is a co-chair of BEPA. The Commission welcomed the provisional political agreement to make all batteries placed on the EU market more sustainable, circular and safe.
Umicore offers battery materials and highly efficient recycling services compliant with the sustainability requirements on carbon footprint, recycled content, and performance and durability, which will be introduced gradually from 2024 onwards.
For an overview of all the association memberships see the Key Memberships list below.
Key memberships |
| A3M (L’Alliance des Minerais, Minéraux et Métaux); Agoria (Belgian multi-sector federation for the technology industry); American European Community Association (AECA); Belgian Alliance for Climate Action (BACA); Belgo Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (BICC&I); Belgian industrial Research and Development (BiR&D); Belgium-Japan Association & Chamber of Commerce (BJA); Drive+ (platform for automotive suppliers and associations to discuss Drive Sustainability Partnership); Eurometaux (European Non-Ferrous Metals Association); European Industrial Research Management Association (EIRMA); European Partnership for Responsible Minerals (EPRM); European Round Table of Industrialists (ERT); ETION Forum for engaged entrepreneurship based in Flanders; Federation of Belgian Industrial Energy Consumers (FEBELIEC); Flemish Network of Enterprises (Voka); Flanders-China Chamber of Commerce (FCCC); Global Legislators for a Balanced Environment (GloBE EU); Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI); The Shift (a Belgian sustainability community); Verbond van Belgische Ondernemingen (VBO); World Economic Forum (WEF); UN Global Compact. |
BatteryBattery Europe Partnership Association (BEPA); Cobalt Institute; Cobalt REACH consortium; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Galvano- und Oberflächentechnik (DGO); Energy Materials Industrial Research Initiative (EMIRI); Essencia; European Association for Battery (ReCharge), Global Battery Alliance (GBA), Hybrid and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (EVB - EV Belgium, ex-AVERE); Nickel Institute; Nickel REACH consortium. |
CatalystsAssociacao dos Fabricantes de Equipamentos para Controle de Emissoes Veiculares da América do Sul (AFEEVAS); Association for Emissions Control by Catalyst (AECC); Catalyst Manufacturers Association, Japan (CMAJ); Committee of Vehicle Emission Control in China (CVEC); Emission Controls Manufacturers Association, India (ECMA); Hydrogen Council; Hydrogen Europe; Manufacturers of Emission Controls Association (MECA); Verband der Automobilindustrie (VDA); Verband der Chemischen Industrie e.V. (VCI); Accessa (Association for the Catalytic Control of Emissions from Stationary Sources to Air). |
RecyclingEuropean Battery Recycling Association (EBRA); European Electronics Recyclers Association (EERA); European Precious Metals Federation (EPMF); Fachvereinigung Edelmetalle (German Precious Metals Association); Global Battery Alliance (GBA); International Platinum Group Metals Association (IPA); International Precious Metals Institute; Minor Metals Trade Association; Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC); The European Association of Advanced Rechargeable Batteries (RECHARGE); London Bullion Market Association (LBMA); London Platinum and Palladium Market (LPPM); International Lithium Association (ILA). |

Advocating for best practices in supply chains
Umicore actively advocates for best practices in the value chain. Our Zero Harm ambition is linked to our continued commitment to sustainably and ethically sourced raw materials. Beyond our long-standing approach to protecting human rights in our supply chain, most notably for ethical cobalt sourcing, and in light of the accelerating transition to electromobility, it is crucial to secure raw materials supply that is reliable and environmentally and socially responsible. Umicore will further build on its long track record of due diligence in the sourcing of critical raw materials. For more, see Sustainable Products & Services.
Umicore was one of the first members of The Global Battery Alliance (GBA), a public-private collaboration platform founded in 2017 at the World Economic Forum to help establish a sustainable battery value chain, bringing together leading international organizations, NGOs, industry actors, academics and multiple governments to align collectively in a pre-competitive approach, to drive systemic change along the entire value chain.
Interacting with communities
Contact with the communities where Umicore operates is the most direct way that we interact with society. Open and transparent dialogue with such communities is an integral part of our stakeholder engagement. Through employment, Umicore also actively contributes to the generation of wealth in all areas where we operate. Although wealth generation is an obvious benefit, the way in which this wealth is generated is also of great importance. Civil society groups periodically declare a stake in our operations and the way we do business. Umicore welcomes such interest and attempts to engage openly and constructively. We always strive to be a top employer wherever we operate. For more information about Umicore as an employer see Employees.
Contributing on a voluntary basis
Umicore makes voluntary contributions at site and Group level to a range of charitable causes. We manage Group-level engagement efforts through a Group Donations Committee that has the mandate to engage with civil society groups and determine the extent of partnerships. As a matter of policy, Umicore does not make donations to political parties or organizations. For more, see Giving back to society.
Umicore paid € 246 million in total taxes on our 2022 operations and with our employees contributed € 119 million in social security payments.
Connecting advocacy to our 2030 RISE Strategy
The year 2022 was a year of change for Umicore. It was the year in which the Umicore 2030 RISE Strategy was unveiled, highlighting exponential growth and opportunities to scale up our business, all while respecting our commitment to society. It was also the year in which our government affairs team took stock of its approach to advocacy translating the new strategy into tangible business implications and advocacy plans. Umicore’s government affairs team are the ambassadors of our business ensuring that we uphold our mission, adhere to our commitments and maximize our positive impact on society. Whether it is by supporting policy developments, building networks, advocating for best practices in supply chains, raising awareness on the issues and trends that affect Umicore strategy our business is guided by the expertise of our government affairs team.
All actions carried out by the team are underpinned by the four key pillars of the new 2030 RISE Strategy.
The work of this team is not only necessary it is fundamental to creating the optimal external conditions for implementing the 2030 RISE Strategy by providing the license to operate; funding to back up the plans for growth; and anticipate the risks and opportunities.
"We are the ambassadors of Umicore and mobilize external stakeholders in support of the 2030 RISE Strategy"Wouter Ghyoot, VP Government Affairs
Moving to a low-carbon society
Accelerating the transition to a low-carbon society requires driving down the cost of clean mobility technologies and clean energy. Electrification of transport and heating processes in industry using electricity generated from renewable sources is crucial to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement. Advanced materials represent a sizeable part of the cost of these clean technologies and are key enablers for a low-carbon society. The advanced materials path from lab to market is long, risky and capital-intensive, so industry welcomes risk-sharing initiatives supporting European industrial leadership. Founded in 2012 by Umicore and other industrial and research organizations, EMIRI (the Energy Materials Industrial Research Initiative) works to raise awareness about the role of advanced materials in everyday life and in the European economy, and advocates for stronger EU-level support for innovation. EMIRI is now the driving force behind the EU’s Advanced Materials Initiative 2030 (AMI2030) that by the end of 2023 should lead to a decision by EU and Member States to launch a publicly funded partnership on advanced materials for the digital and green transition.
Our technologies in clean mobility and resource efficiency are an enabler to mitigate climate change. A more ambitious agenda in terms of climate change is therefore creating market opportunities for Umicore – which is in line with our corporate purpose of integrated value creation. To support ambitious regulations, we demonstrate our technologies and advocate for ambitious targets, because Umicore technology can reach those ambitions. Umicore provides technical insights to support achieving these goals – e.g., by providing science-based targets to authorities. Umicore co-writes longer-term technology roadmaps with regulators, academics and other members of industry.
In resource efficiency, our technologies offer the same functionalities while reducing use of metals. We extract fewer natural resources and re-use metals to create our advanced materials. We emphasize the links between a circular economy and responsible sourcing, resource efficiency and high-quality recycling. Umicore is mindful of the sensitivity of taking positions on matters of public interest and has developed guidelines to do so responsibly through the industry groups to which we are affiliated. Well-developed science and facts form the basis of the opinions and position we take.
We share our knowledge and collaborate with many partners to advance the global transition towards a green and circular economy.
Read how Umicore integrates sustainability into IT.

Launch of the first battery passport
Umicore is a founding member and is represented in the Executive Board of the Global Battery Alliance (GBA) established in 2021, NGOs, academic players, authorities and industrial members worked together with Umicore to develop the first battery passportwith a QR code, which was launched at Davos in January 2023.On a global scale, this passport shows full transparency of the source of the raw materials within a battery and provides a carbon footprint of that battery. A Child Labor Index is to be integrated in the battery passport.
Transparency of a battery’s lifecycle enables consumers, companies and regulators to make well-informed choices, propelling decarbonized electric driving. The Battery Passport is therefore key to reducing climate change.
In addition, Umicore contributes to the WEF Circular Cars working group. This initiative is focused on making the car industry more circular and creating the same functionality with fewer resources. This work explores the impact of a second life battery market, material passports and design-for-recycling concepts in the future automotive and transportation business models.
Enabling ultra-clean transportation
With most developed countries and regions outlining their hydrogen strategies to support their journey towards climate neutrality, Umicore is active in various hydrogen-related advocacy platforms such as Hydrogen Europe, the Hydrogen Council, the European Clean Hydrogen Alliance, the European Raw Materials Alliance, the Electrolyser Partnership, the Energy Materials Industrial Research Initiative (EMIRI) and Waterstofnet. In these platforms, Umicore highlights the key role that advanced materials, such as electrocatalysts, can play in enabling the production of hydrogen by electrolysis and its conversion back into energy using fuel cells. We also highlight the promises of LOHC (liquid organic hydrogen carrier) technology for the transport of hydrogen and our ability to recycle these various hydrogen technologies to recover the precious metals and re-use them in new electrocatalysts.
As a producer of key components of catalytic emission control systems, Umicore is a member of various industry associations worldwide through which, in close collaboration with automotive engineering companies, and we aim to contribute significantly to the portfolio of ultra-clean transportation options of the future, using the most advanced emission control technologies
Engaging for impact
Umicore strives to reach the highest possible impact for society with our products & services portfolio and with the way we do business.
Our technologies in clean mobility and resource efficiency are an enabler to mitigate climate change. Therefore, a more ambitious agenda in terms of climate change is creating market opportunities for Umicore – which is in line with our corporate purpose of integrated value creation. To support ambitious regulations, we demonstrate our technologies and advocate for ambitious targets, because Umicore technology can reach those ambitions. Umicore provides technical insights to support achieving these goals – e.g., by providing science-based targets to authorities. Umicore co-writes longer-term technology roadmaps with regulators, academics and other members of industry.
In resource efficiency, our technologies offer the same functionalities while reducing use of metals. We extract fewer natural resources and re-use metals to create our advanced materials. We emphasize the links between a circular economy and responsible sourcing, resource efficiency and high-quality recycling. Umicore is mindful of the sensitivity of taking positions on matters of public interest and has developed guidelines to do so responsibly through the industry groups to which we are affiliated. Well-developed science and facts form the basis of the opinions and position we take.
Responsible and sustainable sourcing in our supply chains
We leverage our sustainability approach in the value chain, both upstream with our suppliers and downstream with our customers.
As a global materials technology and recycling group, we purchase and recycle minerals and metals for use in a wide range of products and technologies. For our operations to function, we need raw materials, transportation, energy and other goods and services. Sustainable procurement is an essential part of our ambition to be a sustainability champion under our 2030 RISE Strategy. It is also a key driver in our Let’s Go for Zero ambition to cause Zero Harm in our supply chain.
Our approach is shaped by our new Umicore Global Sustainable Sourcing Policy (UGSSP). The UGSSP aims to mitigate supply chain risks, through both direct and indirect procurement. The policy defines our expectations from suppliers and is fully aligned with the Umicore Way, the Umicore Code of Conduct and the Global Framework Agreement on Sustainable Development between Umicore and the IndustriALL Global Union.
We expect our suppliers to be committed to business integrity; to promote the principles of sustainable procurement in their supply chain; to be compliant with local laws; to ensure health and safety; to minimize the impact on climate and the environment; and to respect international human rights law on their own sites and from their own suppliers, including abolishing child and forced labor and eliminating discrimination.
The UGSSP was rolled out during 2022 and will be continued in 2023. To reach our goal, each Business Unit is defining a set of risk-based assessment criteria that include risks to people and the environment. These criteria also enable a risk prioritization approach to focus on highest risk/impact first. By 2025, our aim is to have all identified suppliers adhering to the policy.
The expectations set for all suppliers are complemented by additional dedicated responsible sourcing frameworks for some critical raw materials. Examples are the Sustainable Procurement Framework for Cobalt or the policy on responsible global supply chain of minerals from conflict affected and high-risk areas.
Battery materials
Sustainability of the battery supply chain includes the conditions under which raw materials are extracted and processed, which is why Umicore is committed to responsible sourcing of our battery materials. While Umicore has had a dedicated policy for cobalt in place for the last decade, Umicore also implements due diligence in the supply of other raw materials for batteries, e.g., nickel and lithium. The approach is directly inspired by our experience with cobalt and follows the basic steps of the Sustainable Procurement Framework for Cobalt.

For us, sustainable procurement of cobalt means considering the economic, environmental and social performance of our suppliers in the purchase of materials, as well as the social and environmental impact of the supply chain. To source cobalt, in 2012 we implemented a pioneering Sustainable Procurement Framework for Cobalt and in 2016 were the first to obtain external validation for our ethical procurement and due diligence approach in this area through an annual third-party audit (reported in our annual compliance report).
In 2022, we updated the Cobalt framework for several reasons: to retain our leadership position in this area in line with the new Umicore 2030 RISE Strategy; to extend the scope of ESG requirements; and to align with upcoming regulatory developments. Updates also took account of the heightened awareness that our customers and society at large have regarding activities and their impact on the environment. The Framework follows the principles of the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas but extends beyond the risks described in the OECD Annex II to cover aspects including environmental policies on water, waste, CO2; community engagement, as well as health and safety.
As outlined, Umicore is well aware of the sustainability risks that are linked to the sourcing of cobalt, particularly in the Democratic Republic of Congo both for large-scale industrial mining as for artisanal and small-scale mining. Often, artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) activities are linked to issues such as Human Rights abuses, child labor, poor occupational health and safety conditions. In 2004 Umicore decided to exclude cobalt obtained from ASM from our supply chain due to these high risks. Today, Umicore still does not source any ASM materials, however, we support several initiatives that look into improving conditions of ASMto attain sufficiently high sustainability standards, as well as schooling for children and alternative livelihoods.
To ensure the responsible sourcing and traceability of materials in our supply chain, we carry out a detailed risk assessment of our suppliers, which includes background screening, questionnaires, onsite visits, and if required, enhanced engagement and developing risk mitigation programs with the suppliers. A dedicated cobalt sourcing committee, referred to as the Approval Committee, is responsible for the principles and guidelines in the framework and has overall control and decision-making power. The Approval Committee includes a member of the Umicore management board and the senior management of Sustainability and Supply. For more on Umicore’s efforts to support the development of traceability projects across the industry, see Battery Passport a Re|Source.
Conflict minerals: tin, tantalum, tungsten, gold
In some regions of the world, exploitation of natural resources is used to fund conflict or can be associated with violations of human rights. To prevent materials that are tainted in this way from entering our supply chain, Umicore has adopted a responsible global supply chain of materials from conflict-affected and high-risk areas policy, which is based on the OECD guidelines. In the area of precious metals, this policy is complemented with specific responsible sourcing certification programs (see Responsible Operations below).
Business units purchasing conflict minerals – tin, tantalum, tungsten and gold (also known as 3TG) – to manufacture their products, use the Conflict Mineral Reporting Template from the Responsible Minerals Initiative for their due diligence on the purchased raw materials. All Umicore activities are compliant with the EU Conflict Minerals Regulation (in force since January 1, 2021).

Decarbonizing our purchased materials
One of the key elements of sustainable sourcing is reducing the environmental impact of the supply chain, including Scope 3 emissions. Scope 3 emissions refer to the indirect emissions that occur in the value chain. When looking at our 2019 carbon footprint, Umicore’s Scope 3 emissions are about 10 times the combined amount of our Scopes 1 and 2. The single largest category of emissions comes from upstream activities, specifically in the category “purchased goods and services”.
Umicore has set an ambitious target to reduce the carbon intensity of purchased materials by 42% by 2030. Battery materials and precious metals are the main contributors to the impact of this Scope 3 category. We are engaging with our suppliers to understand their GHG emission profile, ambitions and reduction opportunities to provide our customers with responsible, sustainable and low-carbon products. For more on Scope 3, see Greenhouse Gas Emissions and the Environmental Statements.
Responsible Operations
In addition to our policies on responsible sourcing and the related due diligence, Umicore also pursues responsible sourcing certification wherever appropriate, to highlight our best practices and to provide the necessary documentation to the increasing number of customers seeking assurance on our products. The Umicore internal “Metals and Minerals” working group streamlines and optimizes the efforts required for this increasing customer demand through sharing of best practices.
Umicore sites undergo audit and certification for the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA), the London Platinum and Palladium Market (LPPM), the Responsible Jewelry Council (RJC) and the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI).
When applicable, Umicore amended internal responsible sourcing processes and due diligence procedures to be in line with version 9 of the LBMA Responsible Gold Guidance and version 3 of the LPPM Responsible Platinum and Palladium Sourcing Guidance.
Gold & silver
The London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) manages the accreditation process for all Good Delivery listed refiners for gold and silver. The Responsible Jewelry Council’s (RJC) Chain of Custody (CoC) Standard is applicable to gold and platinum group metals (platinum, palladium and rhodium). Both the RJC Chain of Custody and LBMA Good Delivery accreditations qualify the accredited sites for listing in the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) conformant smelters and refiners.
In 2022, Umicore continued to ensure that operations with gold production are certified as conflict-free. Umicore operations in Hoboken and Pforzheim are certified as conflict-free smelters for gold by the LBMA for the year 2021 and will be audited for 2022 later in 2023. The LBMA also provides certification for responsible silver and the sites of Hoboken, Pforzheim and Bangkok are accredited refiners by the LBMA for 2021 and will be audited for 2022 later in 2023. The Jewelry & Industrial Metals operations in Pforzheim, Vienna and Bangkok are certified as part of the RJC Chain of Custody program for recycled gold and silver. Through mutual recognition of other relevant industry initiatives, the sites in Hoboken, Pforzheim, Vienna and Bangkok are on the RMI Conformant Gold Refiners list.
Our customers are increasingly requesting such guarantees and we provide them with the necessary documentation to attest the conflict-free status of our products.
Platinum, palladium & rhodium
In 2022 the Hoboken site received a Platinum and Palladium Sponge Accreditation Certificate covering the year 2021. The Jewelry & Industrial Metals operations in Pforzheim, Vienna and Bangkok are certified as part of the RJC Chain of Custody program for recycled platinum, palladium and/or rhodium.
Cobalt
In May 2019, Umicore Olen was approved as one of the first Responsible Minerals Initiative-conformant cobalt refinery worldwide, followed by the approval of Umicore’s cobalt operations in Kokkola (Finland). For both sites the re-audit process is currently ongoing and is expected to be finalized in Q1 2023. During this time, the Olen and Kokkola sites remain on the list of RMI conformant refiners.

| LBMA Gold | LBMA Silver | LPPM Platinum & Palladium | RJC Code of Practices | RJC Chain of Custody | RMI conformant Cobalt smelters | RMI conformant Gold smelters and refiners | |
| Bangkok | x | x | x | x | |||
| Hoboken | x (*) | x (*) | x (*) | x (*) | |||
| Kokkola | x (*) | ||||||
| Markham | x | ||||||
| Olen | x (*) | ||||||
| Pforzheim | x (*) | x (*) | x | x | x (*) | ||
| Vienna | x | x | x |
* Audit process for 2022 is still ongoing.
Indirect procurement & transport
Umicore’s worldwide purchasing and transportation teams procure energy and other goods and services referred to as indirect procurement. In 2022, the indirect procurement spend increased compared with the previous year, mainly due to higher energy costs and general prices. The main indirect procurement spend is to be found in Belgium, Germany, Poland, Finland, China & Korea.
As of last year, we do not show any EcoVadis scores of assessments performed by our suppliers. Due to the implementation of a new process in 2022 (see below), it is too early to report figures now. Future comparisons with scores of 2021 and earlier will not be possible as the reference for suppliers having to carry out an EcoVadis assessment has been changed. Although we have changed our processes, the risk-based approach remains the same.
In 2022, we revamped our indirect procurement risk assessment process, bringing it in line with the new Umicore Global Sustainable Sourcing Policy (UGSSP). Prior to 2022, in most regions new suppliers were systematically assessed through a quick scan based on criteria such as spend, geographical location and criticality. Based on this quick scan risk assessment subsequent actions were determined, such as adherence to our procurement charter or, in case of higher risk, the need for an EcoVadis assessment. As of 2022, we will no longer use the quick scan methodology. From now on all new suppliers are identified via a risk assessment, including questions in the area of sustainability. Our critical suppliers, those with the most impact, will be requested to adhere to the UGSSP. After adherence to the UGSSP, we check compliance to the policy by requesting a CSR assessment.
The entire risk assessment process and reporting is currently being digitalized in this new system and will be rolled out further on in the coming months. With this new policy, we bring additional focus on our suppliers and commitment to sustainable practices, which is vital not only for Umicore but also for our societies.
By 2025, all identified suppliers in indirect procurement will be requested to adhere to the UGSSP.
Greening supply chain transportation
In 2022, Umicore developed the foundations of a Sustainable Logistics Roadmap in order to reduce the transport-related emissions within Scope 3. The roadmap focuses among others on calculation methodologies with the aim of aligning with globally recognized methodologies, more sustainable transportation solutions and strategic partnerships with Logistic Service Providers.
Although not specifically linked to our Scope 3 objective and 2030 targets, green logistics is high on our agenda. We are continuously exploring additional solutions for green logistics and increasing our knowledge by following relevant training.
Sustainable Products & Services
Umicore strives to maximize the positive impact on society, through our operations, in our supply chain and with our products and services.
Umicore materials can be found in a variety of applications that deliver solutions for cleaner air and increased e-mobility while our unique closed-loop services turn waste metals into a resource. We provide advanced products that are built on our customers’ specific performance, environmental and sustainable sourcing needs. Beyond this customer-oriented approach, we provide close collaboration across all regions to deliver a sustainable and secure supply of high-quality products and services. Our high level of investment in R&D ensures advanced and efficient production and process technologies that enable our customers to meet the most stringent sustainability demands and ambitions.
Umicore’s diverse workforce brings global perspectives to our innovation and works in proximity to our international customer markets. Our ambition to achieve Net Zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2035 will enable Umicore to offer products with a reduced carbon footprint to our customers.

For more Umicore products and services, visit: umicore.com/products
Revenues from clean mobility & recycling
Umicore’s primary focus in terms of sustainable products and services is to leverage activities that provide solutions for clean mobility and resource scarcity. For many years, Umicore has been emphasizing this focus by disclosing the portion of revenues we gain from clean mobility materials and recycling.
In 2022, 78% of Group revenues (excluding metals) were generated from activities that deliver products or services that are directly linked to clean mobility or recycling. We include the production of automotive catalysts, fuel cell catalysts and battery materials for electrified vehicles, which all contribute to cleaner mobility. For recycling, we consider our refining activities, thereby taking into account the portion of secondary materials processed. We are at a similar level as in 2021, and have increased significantly from 65% in 2016, when we began tracking revenues in this way.
Many of the materials and services making up the remaining 20% of revenues provide answers to specific societal needs such as improved connectivity (materials for high quality glass and displays) or reduced energy consumption (materials for use in energy-efficient lighting such as LEDs).
For EU Taxonomy eligible and aligned activities, see EU Taxonomy.
Measuring impact
To support our ambition to turn sustainability into a greater competitive advantage, it is essential to develop a full understanding of the impact that our products have on the world. These insights can then be leveraged to improve the footprint of our products and services. Umicore’s product life cycle assessments (LCAs) identify the environmental impact of products and services and set a baseline against which improvements can be measured. An LCA is a standardized, science-based tool used to define the degree of environmental impact of a given system or product1. LCAs take into account all phases of the product’s life cycle, including direct and indirect emissions, examine inputs and outputs for each phase, and convert them into an environmental impact measurement.
Building on the opportunities identified in such assessments, we leverage our unique combination of materials chemistry, energy mix and materials mix (raw and recycled) to improve our overall environmental impact and to contribute to lower-carbon mobility. Umicore will continue to develop selective products and services that have specific sustainability benefits and answer the growing sustainability needs of our customers. We are already working closely with customers and have started engaging with suppliers to reduce the upstream footprint of our products.
Among the impact categories calculated in an LCA, the impact of GHGs to climate change, expressed in carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e), is prioritized because of the urgent need to tackle global warming. Until Umicore reaches the Net Zero GHG emissions target, our industrial operations will continue to emit. Our products and recycling services do have, however, a positive impact in terms of GHG emissions in the value chain. First and foremost, as a key element of our closed-loop business model, the recovery of metals from secondary sources provides raw materials with a lower carbon footprint to society; and secondly, rechargeable battery materials accelerate the transition to low-carbon mobility.
In terms of avoided emissions (sometimes referred to as "Scope 4"), Umicore examined in 2022 the activities linked to catalyst materials for fuel cell vehicles, next to the activities already assessed in 2021, i.e., cathode materials for electric mobility and to recycling key raw materials. The relevant avoided emissions for these activities are the GHG emissions. We also analyzed the avoided NOx emissions linked to automotive catalysts. Based on those activities, we have estimated the total avoided GHG and NOx emissions for 2022. In our calculations, a portion of our estimation was not allocated specifically to Umicore, to reflect the estimated shared contribution of the complete value chain. For more details about the assumptions considered for our calculations, see GHG emissions in the Environmental Statements.
For electric mobility, we compared rechargeable batteries for electric vehicles with a medium passenger car with an internal combustion engine running on diesel or gasoline, considering the European split between diesel and gasoline in 2021. Approximately 7.7 million tons of GHG were avoided, taking into account the production of the cathode materials, their processing into batteries, the use of batteries in full electric vehicles and end-of-life recycling.
A similar calculation comparing fuel cell vehicles with internal combustion engines, yields for 2022 approximately 130,000 tons GHG avoided emissions. For our recycling activity, we compared Umicore’s secondary production with the primary production of an equivalent tonnage of each metal considered. The avoided emissions are close to 1.5 million tons of GHGs for 2022.
For automotive catalysts, the calculation is based on comparing gasoline and diesel personal cars as well as heavy-duty diesel vehicles equipped with Euro 6d catalysts with similar vehicles equipped with Euro 5 catalysts. The avoided NOx emissions for the lifetime of cars equipped with Umicore catalysts in 2022 amount to approximately 2.8 million tons.
Given the uncertainties involved in the assumptions, the figures should only be considered as estimates of the potential benefit for society. We aim to refine such calculations in the future, in particular by engaging with our suppliers and by working closely with our customers.

Product stewardship
Umicore’s business model is dedicated to delivering sustainable products and services, and we are committed to leveraging our expertise and resources to developing safe, sustainable, and innovative solutions that enhance the quality of life for people and the planet. That is why our product development is focused on meeting those societal needs.
We evaluate the environmental, health and safety performance of our products through their life cycle to identify and implement improvements – from the supply chain, to up- and downstream production, to recycling or end-of-life – even looking to the future, with substitution planning, and aiming to reduce the use and production of substances of very high concern.
Our commitment to maximizing our positive impact through our products and services includes protecting human health. Transparent communication with our stakeholders on the properties, hazards, safe use and disposal of our products, combined with a deep knowledge of the products and their uses are essential elements of Umicore’s approach to product stewardship. For more, see Management Approach.
Worldwide, Umicore ensures regulatory compliance for the products it puts on the market. For more, see Regulatory and Legal Context. Beyond compliance, Umicore has a systematic approach to the hazard assessment of its portfolio of low volume chemicals, using a hierarchy of sources, from in-house data to publicly available information. The outcomes of the hazard assessments are stored in Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and shared directly with Umicore customers and partners.
Sustainable value chain
To be a preferred sustainable supplier, we work directly with our customers to meet their sustainability/ESG requirements. This involves collaborating with our customers to develop, produce and recycle metal-related materials for material-based solutions tailored to their needs. Ongoing interaction with customers is managed by the business units. In addition to this close contact, all business units have a customer feedback process to gauge customer satisfaction periodically.
We are committed to transparency and as a result, Umicore discloses to a number of third-party sustainable supplier assessments, including EcoVadis and the CDP.

Giving Back To Society
Making a positive difference in our communities, because we care
Umicore seeks to give back to the planet and to contribute to the well-being of the communities in which we operate to be a responsible corporation and good corporate neighbor. We believe that empowering Umicore sites for local sponsorship and donation initiatives will make a positive difference in the communities in which we operate. Umicore’s support may include contributions in kind and releasing staff to work on community-related projects.
While sites determine the specific focus of their own initiatives, the general focus is on supporting and promoting a strong social fabric in the community around the site, with priority given to educational initiatives. The causes we support at site level are often dear to our staff members.
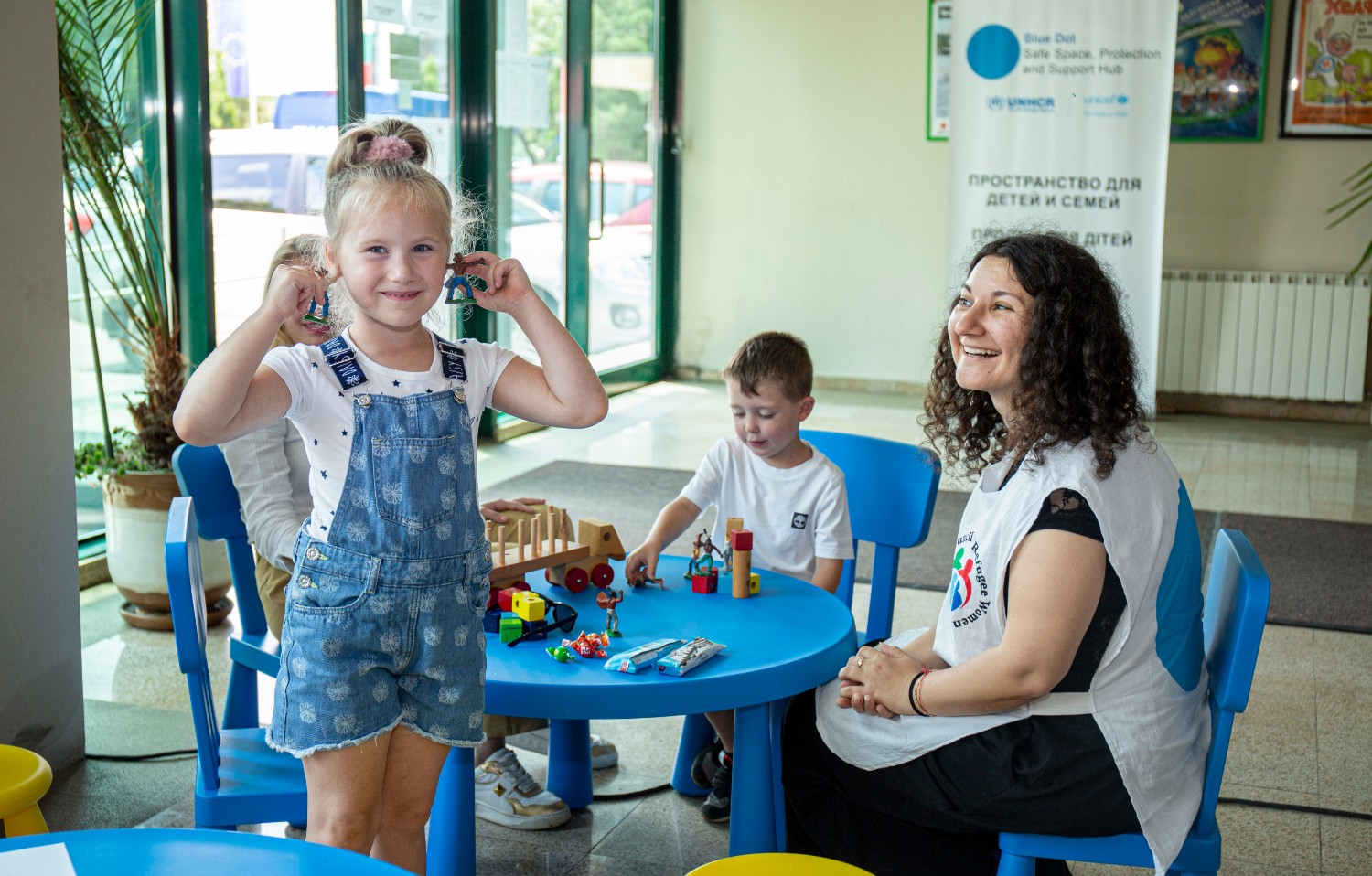

Source: UNICEF
In 2022, our site in Olen (Belgium) supported a local NGO offering disadvantaged adults the opportunity to gain access to skill-enhancing classes such as writing, poetry and computing. Our colleagues in Australia supported recreational activities for disabled children. In Nowa Ruda (Poland), our colleagues organized a collection of used books to give them a second life.
At corporate level, the emphasis is on projects with an international scope with priority given to initiatives with a direct sustainable impact on society or the planet by empowering minorities and communities. Next to disaster relief, the projects supported through our donations all contribute to Umicore’s 2030 RISE Strategy and more specifically our “Sustainability champion” pillar which is built on our Let’s go for Zero ambitions of achieving net zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2035; ensuring zero inequality and zero harm.
Disaster relief: impactful donation for Ukraine
With the ongoing war in Ukraine, Umicore took action to support the victims of the conflict by making a substantial donation to help finance UNICEF’s “Blue Dot Hubs”. With hubs located in strategic places bordering Ukraine, the Blue Dot Hubs can provide support and services to children and their families fleeing the war. They are safe spaces where families can rest and children can play. Refugees can also access a range of services at the Blue Dot Hubs such as mental and psychosocial support, first aid, distribution of emergency supplies, legal aid and counselling.
Umicore also donated locally in the regions around our plants in Nowa Ruda and Nysa, Poland. There we supported the education of Ukrainian students in cooperation with local authorities and NGOs (e.g. The Polish Red Cross and Caritas).
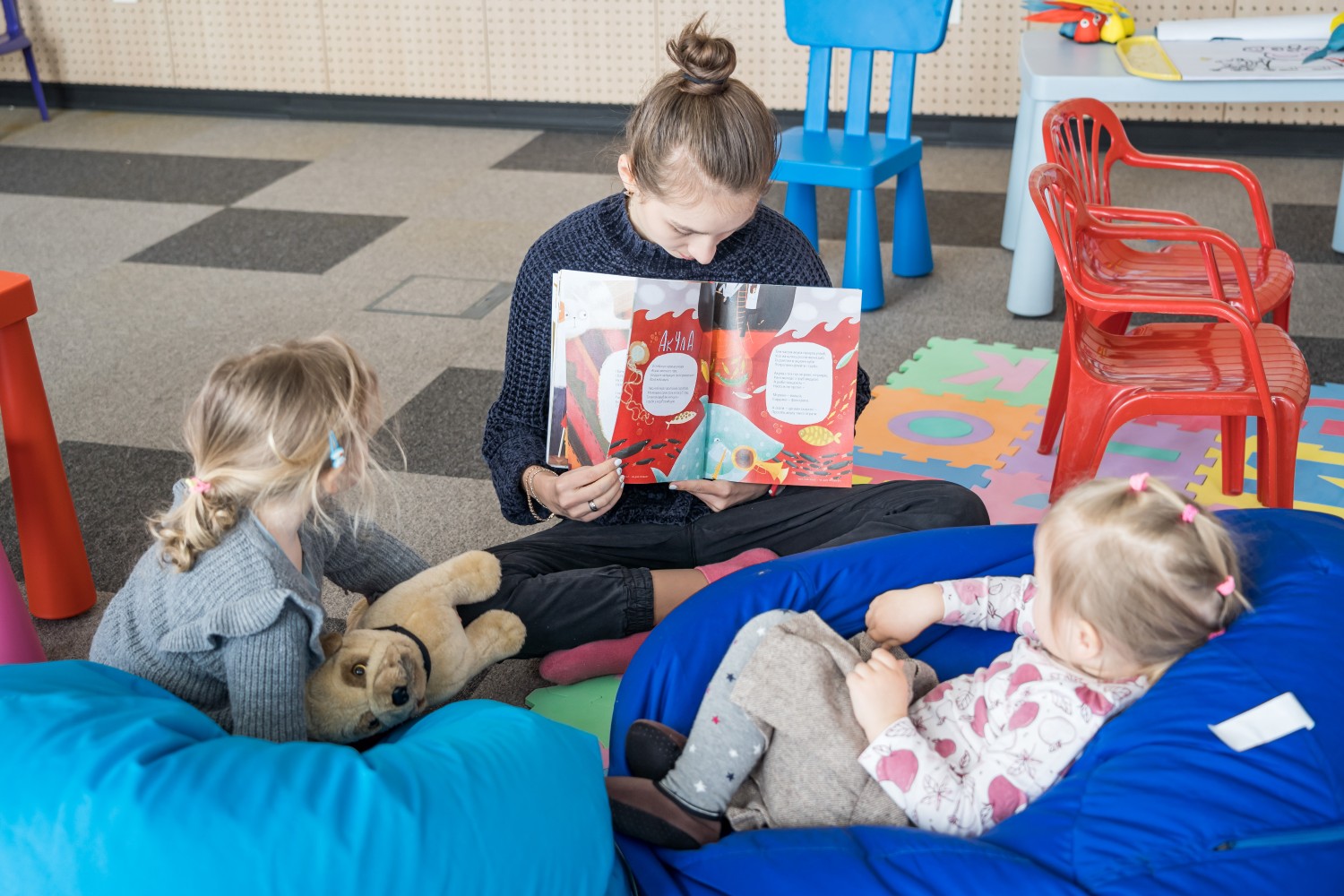

Source: UNICEF
Colleagues around the world have also joined forces to collect goods for Ukraine. In the US and Canada, our colleagues raised funds to purchase relief items for the Ukrainian people. In Hanau, Germany, colleagues bought and packed food, baby and hygiene products, and other essential goods to be transported to the Ukrainian-Polish border; and supported the integration of Ukrainian schoolchildren with the help of music courses and schoolbooks.
Knowledge is the key to building a better world
Educational initiatives are particularly relevant for Umicore as a technology-oriented business. For the past decade, we have been working with UNICEF to reach those children who are in most need. We currently support two long-term projects:
- UNICEF Upshift empowers young people in India by developing the skills they need to enter a labor market characterized by high unemployment.
- STEM education for girls organizes bootcamps and skills sessions around STEM education for girls in Indonesia. STEM – science, technology, engineering and mathematics – are important skills for employment and empowerment.
Entrepreneurship as a force for good
Umicore is a founding member of Entrepreneurs pour Entrepreneurs/ Ondernemers voor Ondernemers (OVO). Established in 2000, the NGO pairs corporate donors with development charities that focus on promoting entrepreneurship in the developing world. Over the years, Umicore and OVO have supported work in many countries. In 2022, we focused on a project in Uganda helping young people in making their food business start-up successful. In El Salvador, we supported technical schools by providing training in electricity and photovoltaic energy.
Umicore employees select their favorite charity
In June 2022, as part of the internal launch of Umicore’s 2030 RISE Strategy, we asked our employees to vote for their favorite charity helping children in need from a selection provided. SOS Children’s Villages, a global charity that provides loving homes for children who have been abandoned and orphaned, gained the most votes, winning the competition. Umicore then donated € 50,000 to the charity with which they were able to develop and implement their new PDP2 digitalization tool. With this tool SOS Children’s Villages can collect data and track families in Burundi and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Tracked indicators cover eight dimensions ranging from accommodation; food security; education; to social and emotional wellbeing. Social workers in the field can now switch from using paperwork to introducing data directly via laptops, tablets, or mobile phones.
Society key figures
| Millions of Euros | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Raw materials cost (excluding water, gas & electricity) | 11,759 | 15,539 | 18,720 | 21,500 | 22,625 |
| Water, gas & electricity cost | 96 | 100 | 100 | 144 | 251 |
| Depreciation & impairments | 227 | 307 | 363 | 339 | 328 |
| Other costs (net) | 516 | 434 | 533 | 532 | 706 |
| Total tax paid | 158 | 107.4 | 98 | 198 | 246 |
| Creditors | 33 | 41 | 58 | 52 | 77 |
| Minority Shareholders | 11 | 11 | 5 | 8 | 3 |
| Shareholders (dividends only) | 181 | 180 | 60 | 181 | 192 |
| Charitable donations | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 2 |
| Employee compensation & benefits | 731 | 776 | 799 | 853 | 907 |
